Arthroscopy
Arthroscopy
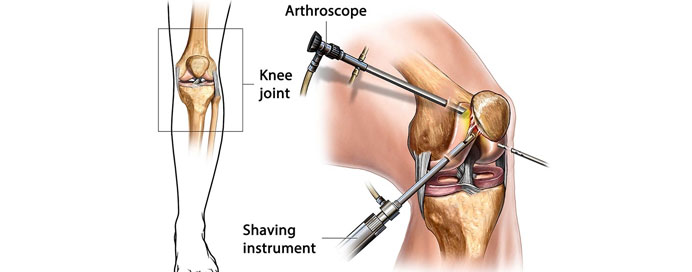
Arthroscopy is a minimally invasive surgical procedure used to diagnose and treat problems within a joint. This procedure involves inserting a thin, flexible tube with a camera (arthroscope) through small incisions near the joint. The camera allows surgeons to visualize the inside of the joint on a screen in real-time. Arthroscopy is commonly performed on joints such as the knee, shoulder, hip, and ankle.
During arthroscopy, surgical instruments can be introduced through additional small incisions if necessary. The benefits of arthroscopy include shorter recovery times, reduced postoperative pain, and smaller scars compared to traditional open surgery.
Arthroscopy is employed for various purposes, including the repair of torn ligaments or cartilage, removal of inflamed tissue or loose bone fragments, and the treatment of conditions like arthritis. It is often an outpatient procedure, and patients typically undergo rehabilitation and physical therapy to optimize joint function postoperatively. Arthroscopy has become a valuable tool in orthopedic surgery, allowing for accurate diagnosis and targeted treatment of joint-related issues with minimal invasiveness.

